Work, Energy, and Power - Topic 2.3
Bite-sized Work, Energy & Power Study Notes for IB Physics HL/SL
Table of Contents
Key point
- Energy is neither created nor destroyed
Conservation of Energy: Energy is neither created nor destroyed, but is only transformed from one form to another.
- A system’s energy may change as a result of interactions with its surroundings
- Mainly: Work done or transfer of thermal energy (heat)
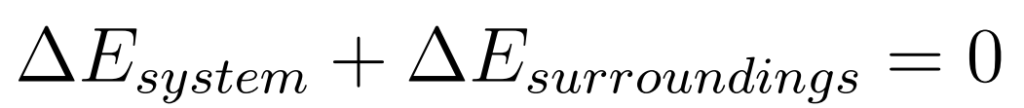
Key point
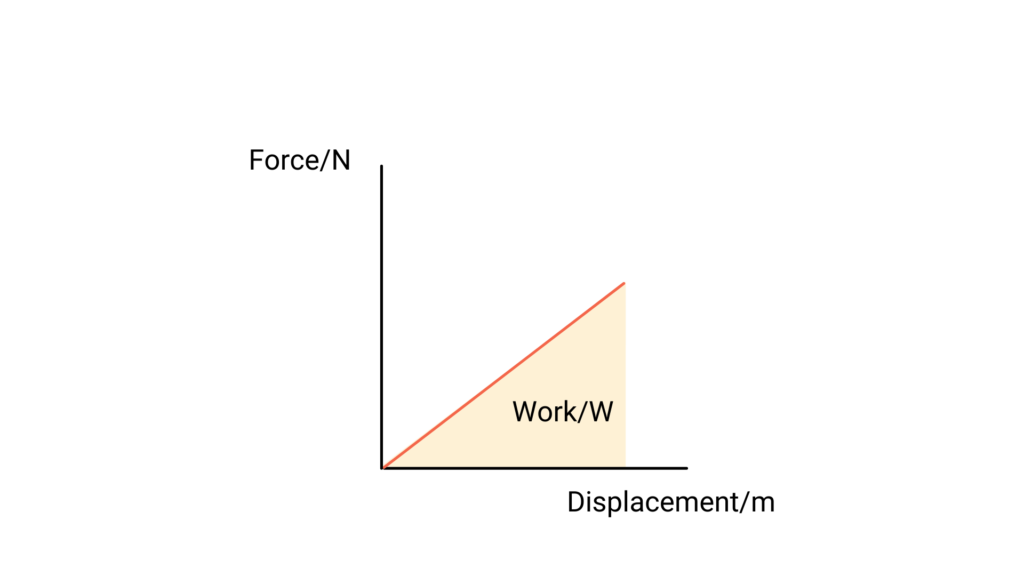
- Work done by a force is the product of the force times the distance travelled
- F = Force
- W = Work
- s = distance
- Θ = angle between force and displacement
- Unit: Joule
- One Joule is the work done by a force of 1 N when it moves a body a distance of 1 m in the direction of the force
- 1 J = 1 Nm
Formula Booklet
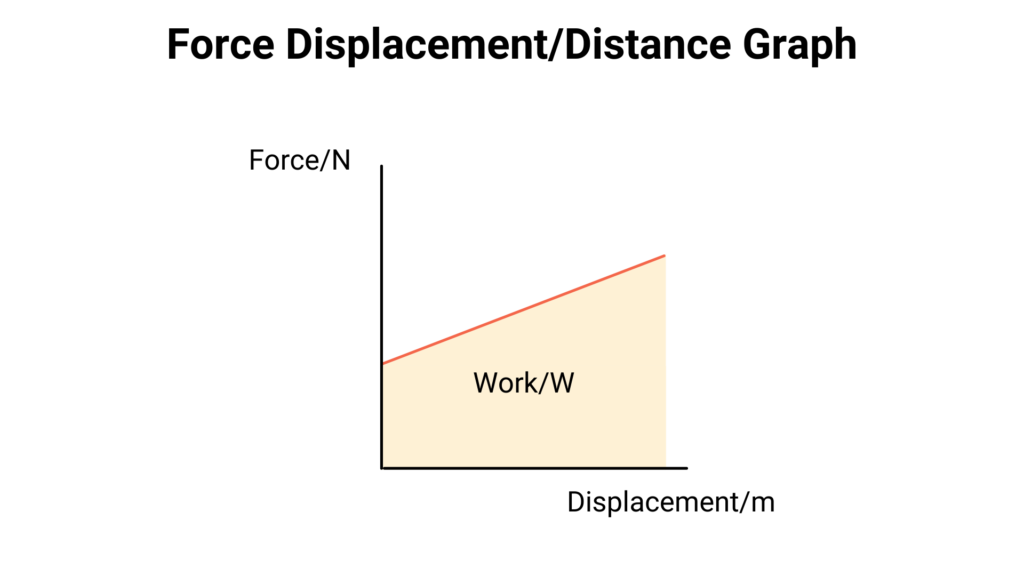
The work done by a force is the area of a force/displacement graph.
Since F = kx and Work is the area under the force-displacement graph the resulting equation is
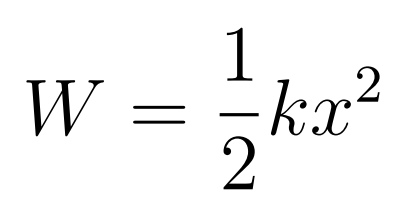
- Work done becomes Elastic Potential
- m = mass
- g = gravity
- s = displacement
- Θ = angle made when the body falls
- Work done by gravity is independent of the path followed
- Work done by gravity depends solely on the vertical distance separating the initial and final positions
- that is true for all conservative forces
Not in Formula Booklet but important
Work done by gravity
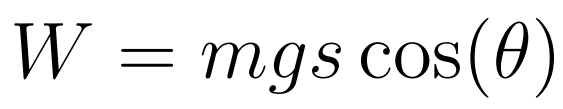
PlusPlusTutors
#1 Online IB Tutoring Experience
- Experienced Tutors
- Recorded Lessons
- Accessible anytime, anywhere
- Personalized Tutor Matching
- Safe & Secure Learning System

Key point
- Mechanical Energy is the energy possessed by an object due to its position and motion
Mechanical Energy is the energy possessed by an object due to its position and its motion.
Potential Energy is the energy of a system due to its position or shape and represents the work done by an external agent in bringing the system to that position or shape.
Kinetic Energy is the energy an object possesses because of its motion.
There are two major kinds of potential energy:
- Elastic Potential Energy is the work done by pulling the spring by an amount x.
- k = spring constant
- x = displacement
Formula Booklet
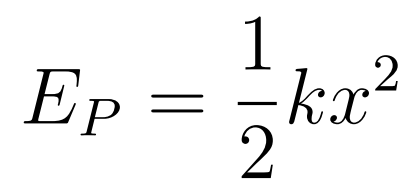
Formula Booklet
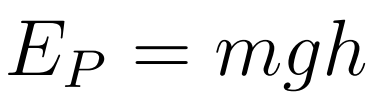
There are two major kinds of potential energy:
- Elastic Potential Energy
- Gravitational Potential Energy is the work done by the moving force in placing the body at a height h above its initial position.
- m = mass
- g = gravitational acceleration
- h = height
Potential Energy is the property of a system, not of an individual particle.
Kinetic Energy is the energy an object possesses due to its motion.
- Kinetic energy is always positive or 0
- Kinetic energy is a scalar
- m = mass
- v = velocity
Formula Booklet
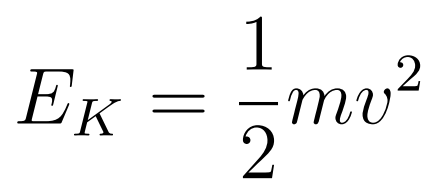
Not in Formula Booklet but important
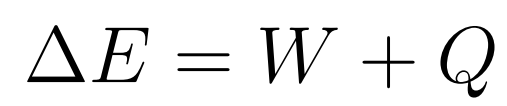
If the system in question is in contact with its surroundings at a different temperature then there will be a transfer of heat, Q.
If there is no contact or no temperature difference, then Q = 0.
For a single particle of mass m following equation is true.
- Notice how when kinetic energy is at its maximum, potential energy must be at its minimum
- This structure is the foundation is almost all energy questions
Not in Formula Booklet but important
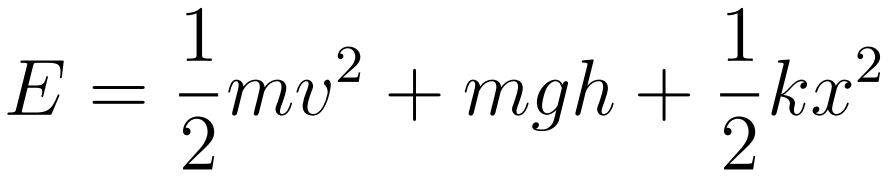
Key points
- The rate at which work is being performed
- The rate at which energy is being transferred
Power is the rate at which work is being performed or the rate at which energy is being transferred.
- When a Quantity of ΔW is performed within a time interval Δt the power developed is given by:
Not in Formula Booklet but important
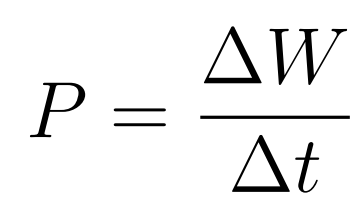
Formula Booklet
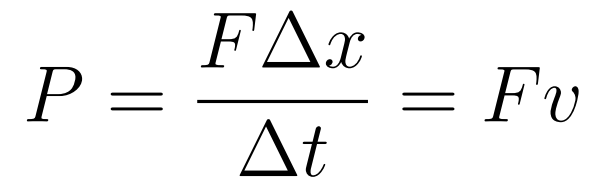
- Rewriting the expression above leaves us with the formula booklet expression.
- Unit: joule per second, which results in watt (W)
- 1 W = 1 J/s
Key point
- Comparison between energy input and energy output
- Rewriting the expression above leaves us with the formula booklet expression.
- The final velocity is equal to initial velocity plus the acceleration the object experienced during a given time interval
Efficiency is the comparison between energy input and energy output.
- Efficiency can not be negative
- Remember the law of conservation of energy
Formula Booklet
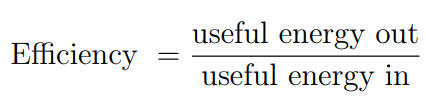
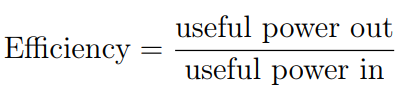
Worksheets
Work, Energy, and Power Worksheet
Questions and Answers
IB Physics Energy Production Questions
Questions
Mechanical Energy Questions (PDF)
Questions
Mechanical Energy Answers (PDF)
Answers
Subscribe to the Inertia Newsletter
IB News, Covid-19 Updates, Deadlines, Tips and Tricks, and Hundreds of Free Resources are Awaiting You!
Features
- Study Notes
- Thousands of IB Questions
- Detailed Answers
- Ask-A-Question System

