Thermal Concepts - Topic 3.1
Bite-sized Thermal Concepts Study Notes for IB Physics HL/SL
Table of Contents

Key point
- Matter consists of very small particles
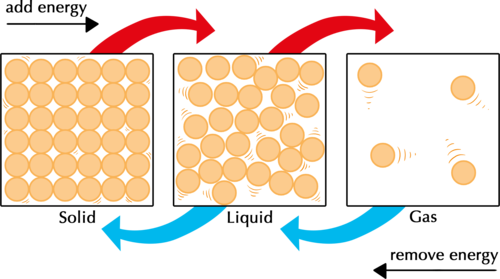
The particle model of matter states that all matter is composed of small particles.
There are three types of states:
- Solid
- Liquid
- Gas
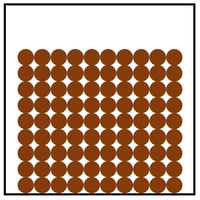
In a solid, particles can be modeled by springs. The strings represent bonds.
- A solid has very strong bonds
- Inter-particle forces are very high
- Particles are in a regular arrangement
- Particles vibrate around a fixed position
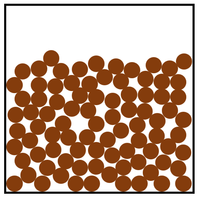
In a liquid, particles will take the shape of the container they are placed in.
- Medium-strong bonds
- Inter-particle forces are somewhat high
- Particles are in a random arrangement
- Particles can slide past one another
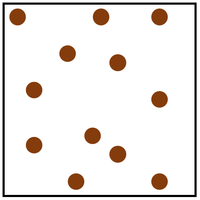
Gas is the least dense state of matter.
- Gas has very weak bonds
- Inter-particle forces are very low
- Particles are in a random arrangement
- Particles are free to move in all directions
Key points
- Temperature is proportional to the random kinetic energy of a molecule
- Lowest possible temperature is the absolute zero
Temperature is a measure of ‘hotness’ or ‘coldness’ of a body.
- Proportional to the random kinetic energy of a molecule
- Kelvin Scale – to illustrate the ‘hotness’ or ‘coldness’ of a body
- Since random kinetic energy can be 0, the temperature can be 0 too – absolute zero
- The magnitude of a Kelvin is the same as that of a degree of Celsius
T (in Kelvin, K) = T (in degrees Celsuis, C) + 273
A Thermometer is used to measure temperature.
- Must possess a property that changes in a predictable way with varying temperature
- When the thermometer is in contact with the substance in question, then a thermal interaction occurs until the thermometer and the substance are in a thermal equilibrium
Key point
- Heat is energy that is transferred between bodies
Heat is the energy that is transferred from one body to another body as a result of a difference in temperature.
- Each Molecule consists of particles
- Kinetic Energy – the speed of vibration
- Potential Energy – the separation between the particles
- Internal Energy – the sum of Kinetic Energy and the inter-particle potential energy
- Heat transferred between a hot and a cold body increases the internal energy of the cold body
- Work done on particles increases the potential energy
- Thus the internal energy can change due to work performed or heat transfer
- Internal Energy, heat, and work are all measured in Joules (J)
- Temperature is a measure of the random kinetic energy of a molecule
Formula Booklet
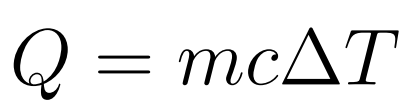
Specific Heat Capacity is the amount of energy needed in order to increase a unit of mass of the object by one kelvin.
- Q = Energy/Heat
- m = mass
- c = specific heat capacity
- ΔT = change in Temperature
Key point
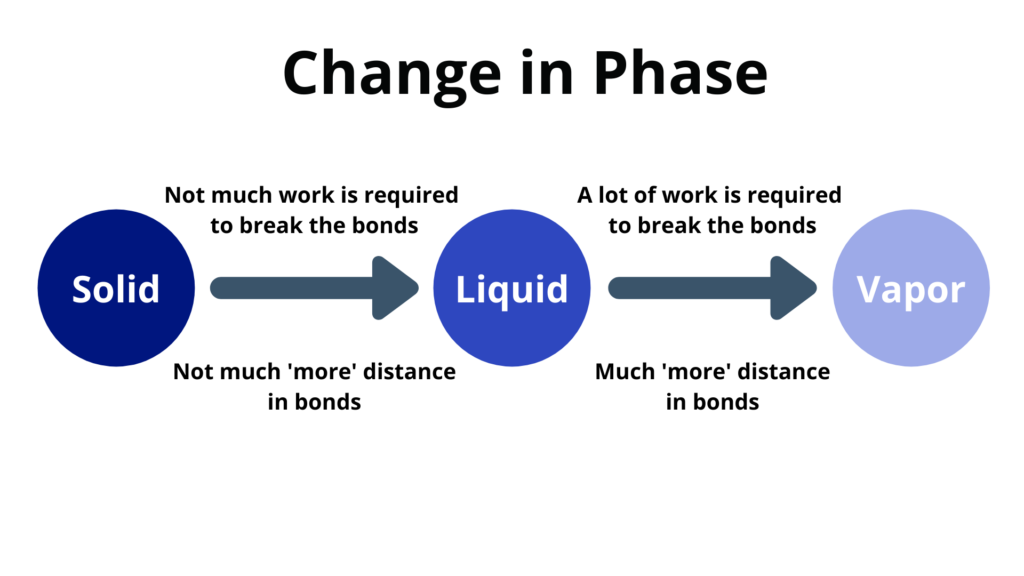
- When heat is provided to a body it doesn’t mean that the body will change its temperature – it may also change its phase
Change of phase happens at a constant temperature.
- Melting – when a solid changes to a liquid
- Freezing – when a liquid changes to a solid
- Vaporization – when a liquid changes to a vapor
- Condensation – when a vapor changes into a liquid
- The heat energy goes into the potential energy instead of the kinetic energy
Formula Booklet
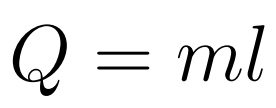
Specific Latent Heat (l) is defined as the amount of energy required to change the phase of a unit mass at a constant temperature.
- Q = Energy/Heat
- l = Specific latent heat
- m = mass
Worksheet/PPT
Key point
- Remember the fundamentals about Physics and its Thermal Concept Laws!
Thermal Concepts Physics Worksheet
Questions/Answers
Subscribe to the Inertia Newsletter
IB News, Covid-19 Updates, Deadlines, Tips and Tricks, and Hundreds of Free Resources are Awaiting You!
Features
- Study Notes
- Thousands of IB Questions
- Detailed Answers
- Ask-A-Question System