Newton's second law in terms of momentum
Key point
- The net force is the rate of change of momentum
Linear Momentum is defined as the product of an object’s mass and velocity.
- Linear Momentum = P
- Linear Momentum is directly proportional to the object’s mass and velocity.
- Momentum is a vector and has a direction of the velocity
- Units: kgm/s or Ns
Formula Booklet
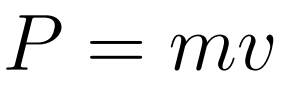
Formula Booklet
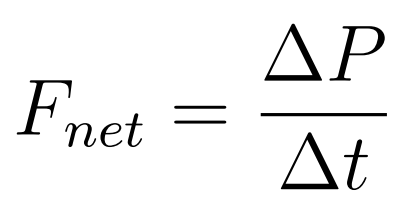
The average net force on a system is equal to the rate of change of the momentum of the system.
- Understand the connection to newton’s second law of motion
Subscribe to the Inertia Newsletter
IB News, Covid-19 Updates, Deadlines, Tips and Tricks, and Hundreds of Free Resources are Awaiting You!
Features
- Study Notes
- Thousands of IB Questions
- Detailed Answers
- Ask-A-Question System

